Friday, February 5, 2010
CELLPHONE
better how much it's means each day
having someone very thoughtful i'd say
I LOVE YOU! not only for the pictures messages you sent
not only for the sweet tone you give my heart
for the graphics you created with your art
you are the best,i've been with you for only a short time
when i think of LOVE,i think of the sweet smile
the tender gaze,the gentle touch that are yours
i think of hope & happiness & togetherness that we share
when i think of LOVE,i think of you!
Wednesday, February 3, 2010
Love is swift, sincere, pious, joyful, generous, strong, patient, faithful, prudent, long-suffering, courageous, and never seeking its own; for wheresoever a person seeketh his own, there he falleth from love.
Destiny is not a matter of chance, it is a matter of choice; it is not a thing to be waited for, it is a thing to be achieved.
Destiny is an absolutely definite and inexorable ruler. Physical ability and moral determination count for nothing. It is impossible to perform the simplest act when the gods say ''no.'' I have no idea how they bring pressure to bear on such occasions; I only know that it is irresistible.
Love is as much of an object as an obsession, everybody wants it, everybody seeks it, but few ever achieve it, those who do will cherish it, be lost in it, and among all, never... never forget it.
Love feels no burden, regards not labors, strives toward more than it attains, argues not of impossibility, since it believes that it may and can do all things. Therefore it avails for all things, and fulfils and accomplishes much where one not a lover falls and lies helpless.
What is Love?
“Love never claims, it ever gives. Love ever suffers, never resents never revenges itself.”
Love is patient, love is kind. It does not envy, it does not boast, it is not proud. It is not rude, it is not self-seeking, it is not easily angered, it keeps no record of wrongs. Love does not delight in evil but rejoices with the truth. It always protects, always trusts, always hopes, always perseveres.”
Love is that condition in which the happiness of another person is essential to your own
“Love never claims, it ever gives.”
My heart to you is given: Oh, do give yours to me; Well lock them up together, And throw away the key.”
Romantic love reaches out in little ways, showing attention and admiration. Romantic love remembers what pleases a woman, what excites her, and what surprises her. Its actions whisper: you are the most special person in my life.”
Inside the heart of each and every one of us there is a longing to be understood by someone who really cares. When a person is understood, he or she can put up with almost anything in the world.”
a heartbreak isnt always as Loud as a bomb exploding,sometimes it could be as quiet as a feather falling,and the most painful thing is...NOBODY hears it..but you...
Letting go,.doesnt mean "its over"..Breaking up,doesnt mean "you had enough"..instead, its a good reason as saying,I dont want you to suffer, Go on..you deserve someone better..
do you know that"i trust u"is better compliment than"i love you"?because you may not always trust the person u love but u can always love the person u trust!
what if u dont believe in LOVE?then someone teaches u how..then u fall 4 himand U believe, but...what if..he's not supposed to love you?only to teach u???
TO ONE'S WHO LOVED
Thursday, January 28, 2010
Network topology is the physical interconnections of the elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network.A local area network (LAN) is one example of a network that exhibits both a physical topology and a logical topology.
2.Examples of Network Topology, their Definition and post example picture.
Star topology
Also known as a star network, a star topology is one of the most common network setups where each of the devices and computers on a network connect to a central hub. A major disadvantage of this type of network topology is that if the central hub fails, all computers connected to that hub would be disconnected. Below is a visual example of a simple computer setup on a network using the star topology.

Ring topology
Also known as a ring network, the ring topology is a type of computer network configuration where each network computer and device are connected to each other forming a large circle (or similar shape). Each packet is sent around the ring until it reaches its final destination. Today, the ring topology is seldom used. Below is a visual example of a simple computer setup on a network using a ring topology.

Mesh topology
A type of network setup where each of the computers and network devices are interconnected with one another, allowing for most transmissions to be distributed, even if one of the connections go down. This type of topology is not commonly used for most computer networks as it is difficult and expensive to have redundant connection to every computer. However, this type of topology is commonly used for wireless networks. Below is a visual example of a simple computer setup on a network using a mesh topology.

Tree topology
Also known as a star bus topology, tree topology is one of the most common types of network setups that is similar to a bus topology and a star topology. A tree topology connects multiple star networks to other star networks. Below is a visual example of a simple computer setup on a network using the star topology.

3. What is OSI Layer?
Short for Open System Interconnection, OSI is a network model developed by ISO in 1978 where peer-to-peer communications are divided into seven layers. Each layer performs a specific task or tasks, and builds upon the preceding layer until the communications are complete. Below are the purposes of each of the seven layers.
4. Examples of OSI Layer, their definition in order.
1 - Physical layer - responsible for the electrical, mechanical and timing across the link.
2 - Data link layer (also known as the link layer) - responsible for transmitting data across a link.
3 - Network layer - responsible for routing information through the network and allowing systems to communicate.
4 - Transport layer - responsible for transferring information between endpoints on the network and deals with errors such as lost or duplicate packets.
5 - Session layer - responsible for managing a session between two applications.
6 - Presentation layer - responsible for the data formatting and display, allowing for compatibility.
7 - Application layer - responsible for user interaction. An example of an OSI application is the FTAM.
5. What is Networking?
In the world of computers, networking is the practice of linking two or more computing devices together for the purpose of sharing data. Networks are built with a mix of computer hardware and computer software.
6. Example of Networking, Post at least 5 examples with picture.
Local area network
A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as home, school, computer laboratory, office building, or closely positioned group of buildings. Each computer or device on the network is a node. Current wired LANs are most likely to be based on Ethernet technology, although new standards like ITU-T G.hn also provide a way to create a wired LAN using existing home wires (coaxial cables, phone lines and power lines)

Home area network
A home area network (HAN) or home hetwork is a residential local area network. It is used for communication between digital devices typically deployed in the home, usually a small number of personal computers and accessories, such as printers and mobile computing devices. An important function is the sharing of Internet access, often a broadband service through a CATV or Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) provider.
Storage area network
A storage area network is an network architecture to attach remote computer storage devices (such as disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes) to servers in such a way that the devices appear as locally attached to the operating system. A SAN typically is its own network of storage devices that are generally not accessible through the regular network by regular devices. The cost and complexity of SANs has dropped in recent years, resulting in much wider adoption across both enterprise and small to medium sized business environments.

Campus area network
A campus area network (CAN) is a computer network made up of an interconnection of local area networks (LANs) within a limited geographical area. It can be considered one form of a metropolitan area network, specific to an academic setting.
In the case of a university campus-based campus area network, the network is likely to link a variety of campus buildings including; academic departments, the university library and student residence halls. A campus area network is larger than a local area network but smaller than a wide area network (WAN) (in some cases).\

Metropolitan area network
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network that connects two or more local area networks or campus area networks together but does not extend beyond the boundaries of the immediate town/city. Routers, switches and hubs are connected to create a metropolitan area network.

NIC Cards
The Network Interface Card (NIC) is a circuit board that is physically installed within an active network node, such as a computer, server, or printer. The NIC is an adapter that controls the exchange of information between the network and the user. Newer NICs are increasingly pre-installed and have the ability to automatically configure to match the speed of the network to which they are connected. For example, if a workstation is attached to a switch on a dedicated connection, the adapter may configure itself to run full-duplex (both talking and listening at the same time) without fear of collisions.
A hub is a box that is used to gather groups of PCs together at a central location with 10BaseT cabling. If you're networking a small group of computers together, you may be able to get  by with a hub, some 10BaseT cables, and a handful of network adapters. Larger networks often use a thin coax "backbone" that connects a row of 10BaseT hubs together. Each hub, in turn, may connect a handful of computer together using 10BaseT cabling, which allows you to build networks of tens, hundreds, or thousands of nodes.
by with a hub, some 10BaseT cables, and a handful of network adapters. Larger networks often use a thin coax "backbone" that connects a row of 10BaseT hubs together. Each hub, in turn, may connect a handful of computer together using 10BaseT cabling, which allows you to build networks of tens, hundreds, or thousands of nodes.
It is very common to see classrooms operating on this type. It is also slow and transfers 10 Megabits (not Megabytes) per second. The category 3 unshielded twisted pair can be used here but if you are just setting up "CAT5" is recommended to save time and money in the future. This is the most common type used in the school system today and uses unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and RJ-45 connectors (low cost phone wire and jacks) to connect users to a hub. The most common type of topology used is a star pattern, so that each node has its own separate segment. This type is very easy to trouble shoot thus lends itself to the school system where technicians are sometimes few and far between.

| Cable/DSL |
Typically DSL and Cable Modems connect to the carrier on one side and a modem on the other. Essentially you must discover the type of system your school uses to decide how to hook-up from there. This is the only type of system going into the home and thus will be of interest to you for that reason. The cable and the DSL lines are probably going to be 10Megabit since that is faster than any of the providers of this service are at this time.

The college and large school divisions are on optic lines which much improves there speed etc. but will not affect us for our discussions. We will leave this until another time.

| Firewalls Basic security to control the flow of data in and out of a network. For our purposes this is controlled by the server that brings all connectivity to computers outside of the classroom. If this were a home cable or DSL line then you would want to install a firewall (software) that would control what other people on the internet can see in your personal computer. |

Bridges
A bridge device filters data traffic at a network boundary.Bridges have a single input and a single output port.They differ from repeaters in that they can interpret the data they retransmit.

Gateways
A network gateway is an internetworking system, a system that joins two networks together. A network gateway can be implemented completely in software, completely in hardware, or as a combination of the two. Depending on their implementation, network gateways can operate at any level of the OSI model from application protocols to low-level signaling.

Routers
A router is a multiport connectivity device that can integrate LANs and WANs running at different transmission speeds and using a variety of protocols. Routers operate at the Network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI Model. Routers have been slower than switches or bridges because they pay attention to information in Layers 3 and higher, such as protocols and logical addresses. Consequently, unlike bridges and Layer 2 switches, routers are protocol-dependent.They must be designed or configured to recognize a certain protocol before they can forward data transmitted using that protocol.

Switches
A network switch is a small hardware device that joins multiple computers together within one local area network (LAN). Technically, network switches operate at layer two (Data Link Layer) of the OSI model.

8. Example of networking cables and their functions, post at least 10 w/ picture.
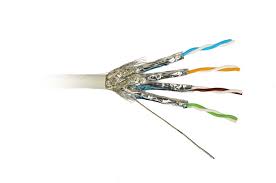
Twisted pair cabling-is a type of wiring in which two conductors (the forward and
return conductors of a single circuit) are twisted together for the purposes of canceling
out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources; for instance,
electromagnetic radiation from Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cables, and crosstalk
between neighboring pairs.
Coaxial cable-or coax, is an electrical cable with an inner conductor surrounded by a
tubular insulating layer typically of a flexible material with a high dielectric constant,
all of which are surrounded by a conductive layer called the shield (typically of fine
woven wire for flexibility, or of a thin metallic foil), and finally covered with a thin
insulating layer on the outside. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the
outer shield sharing the same geometric axis.

Fiber-optic-communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to
another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. The light forms an
electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. First developed
in the 1970s, fiber-optic communication systems have revolutionized the telecommunications
industry and have played a major role in the advent of the Information Age. Because of its
advantages over electrical transmission, optical fibers have largely replaced copper wire
communications in core networks in the developed world.

Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
UTP cable is a medium that is composed of pairs of wires (see Figure 8-1). UTP cable is used in a variety of networks. Each of the eight individual copper wires in UTP cable \is covered by an insulating material. In addition, the wires in each pair are twisted around each other. UTP cable relies solely on the cancellation effect produced by the twisted wire pairs to limit signal degradation caused by electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). To further reduce crosstalk between the pairs in UTP cable, the number of twists in the wire pairs varies. UTP cable must follow precise specifications governing how many twists or braids are permitted per meter (3.28 feet) of cable.

5.) Shielded Twisted-Pair Cable
Shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable combines the techniques of shielding, cancellation, and wire twisting. Each pair of wires is wrapped in a metallic foil. The four pairs of wires then are wrapped in an overall metallic braid or foil, usually 150-ohm cable. As specified for use in Ethernet network installations, STP reduces electrical noise both within the cable (pair-to-pair coupling, or crosstalk) and from outside the cable (EMI and RFI). STP usually is installed with STP data connector, which is created especially for the STP cable. However, STP cabling also can use the same RJ connectors that UTP uses.

Patch cable-
A patch cable is an electrical or optical cable, used to connect one electronic or optical device to another for signal routing. Devices of different types (ie: a switch connected to a computer, or switch to router) are connected with patch cords. It is a very fast connection speed. Patch cords are usually produced in many different colors so as to be easily distinguishable[2], and are relatively short, perhaps no longer than two Ethernet crossover cable.

Ethernet crossover cable
is a type of Ethernet cable used to connect computing devices together directly where they would normally be connected via a network switch, hub or router, such as directly connecting two personal computers via their network adapters.

Power lines
Although power wires are not designed for networking applications, new technologies like Power line communication allows these wires to also be used to interconnect home computers, peripherals or other networked consumer products. On December 2008, the ITU-T adopted Recommendation G.hn/G.9960 as the first worldwide standard for high-speed powerline communications[3]. G.hn also specifies communications over phonelines and coaxial wiring.

Plenum cable
is cable that is laid in the plenum spaces of buildings. The plenum (pronounced /ˈplɛnəm/) is the space that can facilitate air circulation for heating and air conditioning systems, by providing pathways for either heated/conditioned or return airflows. Space between the structural ceiling and the dropped ceiling or under a raised floor is typically considered plenum; however, some drop ceiling designs create a tight seal that does not allow for airflow and therefore may not be considered a plenum air-handling space.

Audio multi-core cable
A multicore cable "snake" helps sound engineers to route a number of signals without having to have a tangled mess of individual cables
Used in the audio recording and sound reinforcement fields, an audio multicore cable (most commonly known as a snake cable or just a snake) is a compact cable, typically about the diameter of a coin, which contains from 4 to 56 individual shielded pair microphone cables all housed by one rugged, heavy-duty common outer jacket. Each end of the multicore cable terminates in a "tail", which contains either a patchbay for female XLR or 1/4" jacks or male plugs.

THE END!
Tuesday, January 26, 2010
THANK YOU
effort you've shown me
the war company you've given me
and most of all the warm friendship
i've encounter with you
i was never inform that you'll come into my life
but just the same
i thank GOD for giving you to me a person
who makes me smile
but someone who accept
just the way i am





